The network need not be a mystery. Learn how to find evidence of network Windows Registry from DFIR expert Chris Ray.
Let’s get to it!
Jump to…
What Is “Network Evidence” in the Windows Registry?
Forensic Relevance of “Network Evidence”
Where to Find Evidence of Network Windows Registry
Keep Learning Registry Forensics
What Is “Network Evidence” in the Windows Registry?
Network evidence in the Windows Registry refers to the traces, configurations, and historical data related to a system’s network activity.
This evidence is embedded in various Registry hives and reveals:
| Data Found in Windows Registry |
|---|
|
This evidence is scattered across SYSTEM, SOFTWARE, and user-specific hives, and can be correlated with other system artifacts (event logs, file access, etc.).
Forensic Relevance of “Network Evidence”
Network data in the Windows Registry can be crucial for:
| Attribution and Presence |
|
| Timeline Construction |
|
| System Configuration and Misuse |
|
| Malware and Persistence |
|
Where to Find Evidence of Network Windows Registry
Network Interface Information
Key information you can get network interface artifacts:
- IP configuration info for each interface.
- MAC address for each interface.
- List of interfaces installed on the system.
Let’s look at each in detail:
IP Config Info for Each Interface
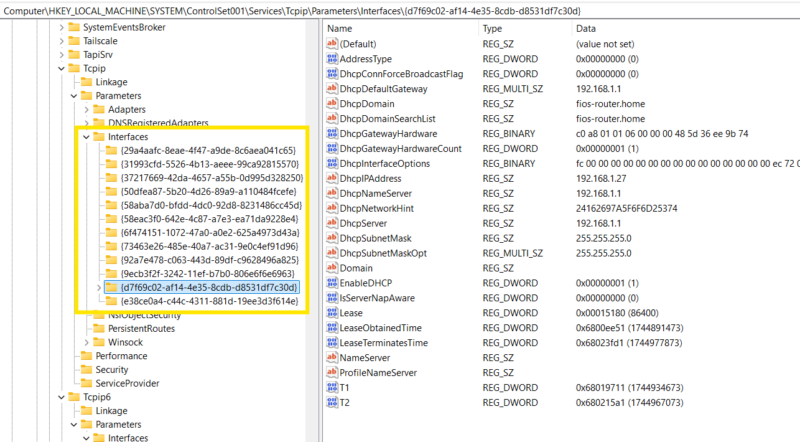
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\
Each subkey represents IP configuration data for an interface. The subkey name represents the interface GUID used to uniquely identify that interface and can be used to correlate information between other artifacts.
Key data each interface can contain:
| Info | Notes |
|---|---|
| Was IP Info Statically/ Dynamically Assigned |
|
| IP Address |
|
| SubnetMask |
|
| DHCP Leasing Info |
|
| DNS Server |
|
| DNS Connection suffix |
|
MAC Address for Each Interface
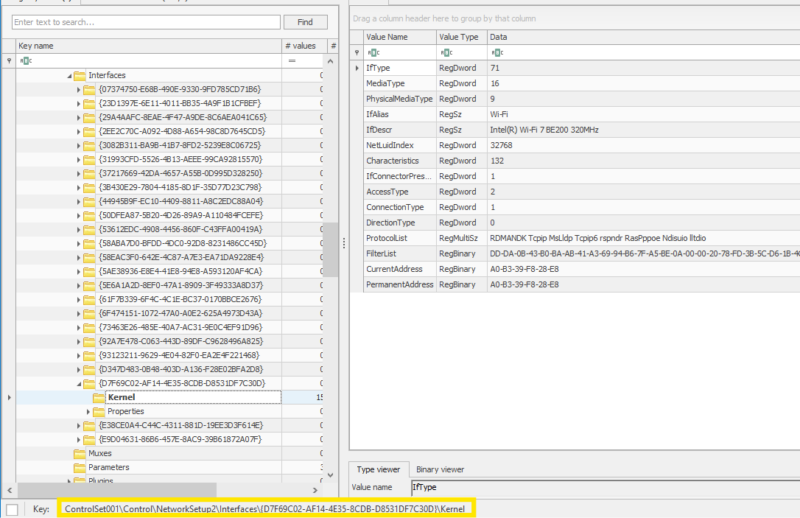
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\NetworkSetup2\Interfaces\{INTERFACE_GUID}\Kernel
Key info:
| Info | Notes |
|---|---|
| MAC Address information |
|
| Interface Description |
|
| Interface Name |
|
NOTE
This information can correlate with the previous information by mapping interface GUIDs.
List of Interfaces Installed on System
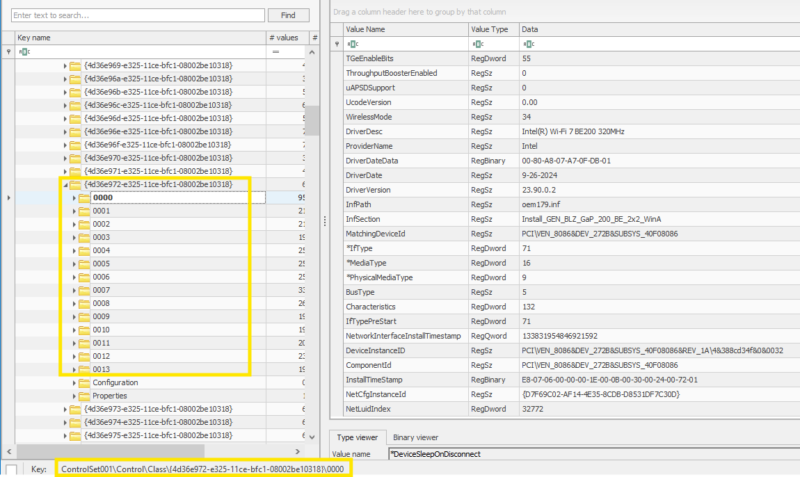
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Class\{4d36e972-e325-11ce-bfc1-08002be10318}
Key details:
- Each subkey following the pattern XXXX where X is all numbers indicates an interface.
- To map this data to other data use “NetCfgInstanceId” as interface GUID.
- There is a wealth of technical info here regarding interfaces such as Driver version, driver install date, install timestamp, adapter model, interface enabled, etc.
NOTES
ControlSet001 can be replaced with any other control set. To find the active control set look at HKLM\SYSTEM\Select. The value “current” tells you the number of the current control set.
TcpIP key is specific to IPv4 settings. There is a Tcpipv6 subkey as well for ipv6 settings although we have not seen as much useful information come out of this key from brief testing but we also did not have a full IPV6 environment setup.
To learn more about these keys, review the Registry Explorer plugins for each of them:
RegRipper3 also has plugins for these Registry keys as well:
Connected Networks
Key info you can get from connected network artifacts:
- Names of networks the system has connected to (wired and wireless)
- First and last connection times for those networks
- Gateway MAC address
- DNS connection suffix
Let’s look at the 2 locations where you can find this data:
Location #1
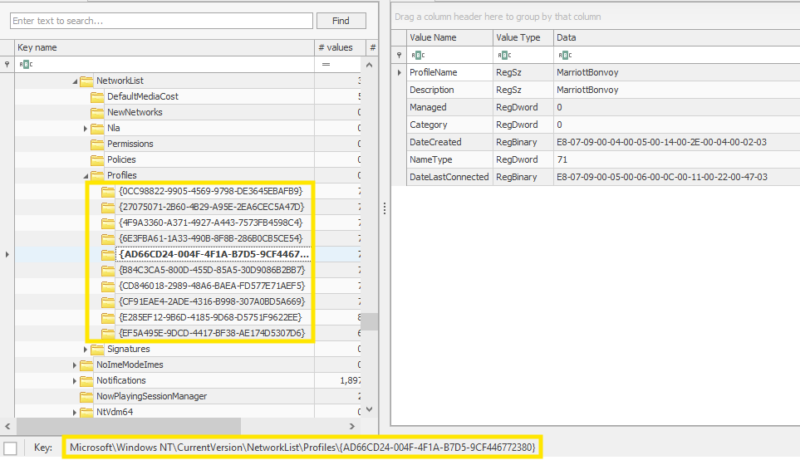
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\NetworkList\Profiles\
Each subkey represents metadata regarding a network the system had joined at some point in time. Subkey names is a GUID that can be used to correlate with other data within Profiles key.
Important info you can get from this key:
| Info | Notes |
|---|---|
| ProfileName |
|
| Description |
|
| DateCreated |
|
| DateLastConnected |
|
| Category |
|
Location #2
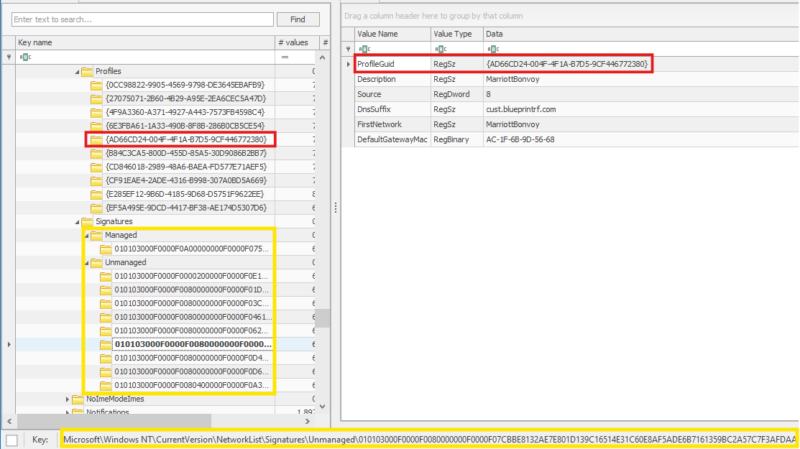
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\NetworkList\Profiles\Signatures\*\
Each subkey under Managed or Unmanaged will represent some additional metadata about a joined network.
Important info you can get from this key:
- ProfileGUID: Used to correlate data in this key to previously mentioned Profiles key.
- DNS suffix associated with network connection.
- Default gateway MAC address.
| Wi-Fi Passwords and Wireless Config |
|---|
While the registry stores general profile info, saved Wi-Fi passwords are stored separately:
netsh wlan show profiles name="*" key=clear This command exposes:
|
You can learn more about this key and the data that can be parsed from it in the Registry Explorer plugin here or the RegRipper3 plugin here.
Windows Firewall Rules
Key info you can get firewall rules:
Firewall Config Settings
- Firewall enabled/disabled for various network profiles (domain/private/public).
- Firewall logging location/size.
- Firewall audit settings.
- Excluded interfaces.*
Firewall Rules
- Rules status: Enabled or disabled.
- Rule definition: What does the rule do?
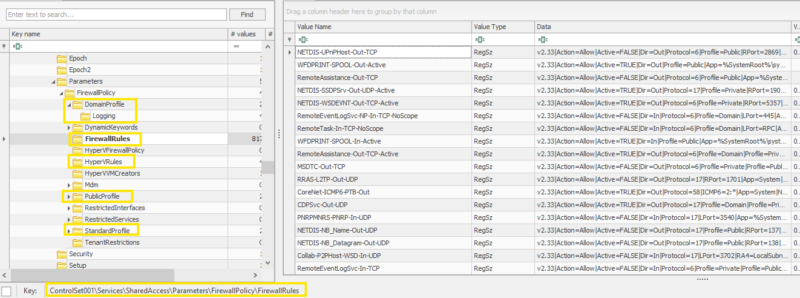
Locations
Firewall settings related to domain network profiles
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\DomainProfile
Firewall settings related to private network profiles
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile
Firewall settings related to public network profiles
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\PublicProfile
Windows firewall rules
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\FirewallRules
Firewall rules for HyperV**
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\HyperVRules
NOTES
* Windows firewall can be enabled while still not protecting an interface if it’s on interface exclusion list.
** Example: If you have WSL and running an Ubuntu VM, you may have rules under this key.
You can learn more about this key and the data parsed from it in the Registry Explorer plugin here
Other Notable Areas of Interest
| Recent Network Shares and Mapped Drives |
|---|
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\MountPoints2\ Tracks mapped network drives and shared folder access. |
| Remote Desktop Connection History |
|---|
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers\ Logs details of remote desktop connections, including IP addresses and usernames. |
| Proxy Server Settings |
|---|
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ Contains proxy configs that may indicate attempts to route traffic through external servers. |
| Shellbags |
|---|
| Shell bags can contain UNC-based folder paths. You can read all about shellbags in our shellbags forensic blog. |
Keep Learning Registry Forensics
This blog post has covered how to find evidence of network Windows Registry. If you found it helpful, we’re writing a whole series on Windows registry forensics you might want to check out.
Here’s the rest:
- UserAssist Forensics
- Shellbags Forensics
- RunMRU Forensics
- MUICache Forensics
- Registry Forensics Tool Guide 2025
Other resources on Network evidence in the Registry:
- The Windows Incident Response Blog: Network Artifacts found in the Registry
- Forensafe: Investigating Windows Network Interfaces
- GIAC: Wireless Networks and the Windows Registry – Just where has your computer been?
