ShimCache and AmCache have lots to offer investigators.
But they’re tricky, too.
Learn the ins and outs of these artifacts from DFIR expert Chris Ray.
Let’s get to it!
Jump to…
Intro to ShimCache and AmCache
Understanding AmCache
Understanding ShimCache
Data Captured by AmCache
Data Captured by ShimCache
AmCache vs. ShimCache
Tools for Analysis
Other Application Compatibility Artifacts
Intro to ShimCache and AmCache
The Windows Application Compatibility (Shim) Infrastructure is a complex and powerful feature that enables older applications to run on newer systems using a form of API hooking.
Metadata is stored on PE files of interest (executed, viewed by user, etc.) and installed applications to allow the shimming infrastructure to work smoothly. As a result, the locations where Windows stores this metadata became key forensic artifacts.
2 most notable:
- ShimCache
- AmCache
From an investigator’s perspective, these artifacts provide a trove of information available by default on all modern systems. This is in contrast to other high-value artifacts like Prefetch (disabled by default on servers) and process auditing (disabled by default), which may not be available.
We will dive into each of these artifacts in the following section below.
But, at a high level, both artifacts provide the following:
| Evidence | Notes |
|---|---|
| Existence | All entries can prove a file once existed at a recorded location. |
| Execution | Due to the complex nature of these artifacts, it’s best to think of this data under evidence of existence rather than evidence of execution. In certain scenarios you can show a file executed with a high degree of confidence, but should never be the definitive proof that something ran. |
| App install | AmCache only. |
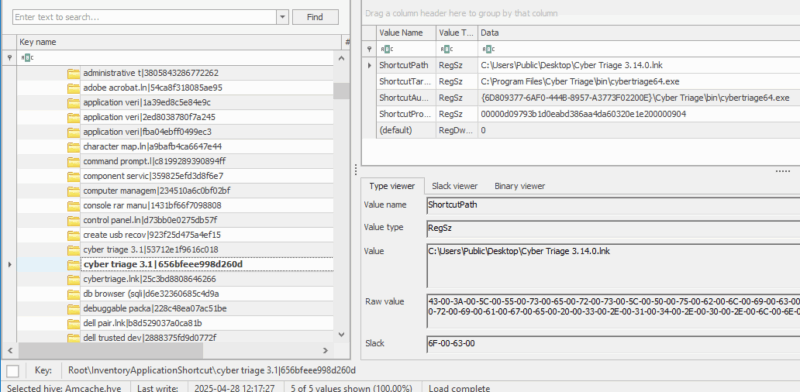
Understanding AmCache
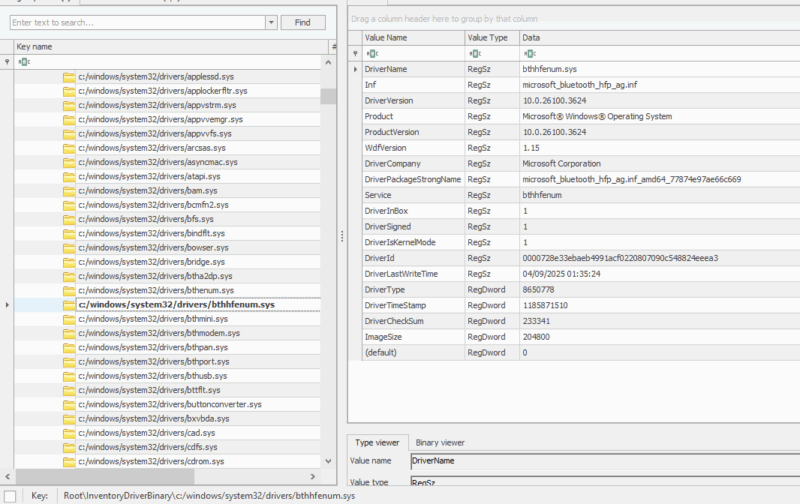
AmCache is part of the Windows shimming infrastructure and was designed to enhance the application compatibility experience. The data is stored in a registry hive (REGF formatted file), which is not part of the Windows Registry. Amcache logs extensive metadata related to installed applications, programs that exist or have been executed, drivers loaded, and much more.
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Newer location | C:\Windows\AppCompat\Programs\Amcache.hve |
| Older location* | C:\AppCompat\Programs\RecentFileCache.bcf |
| Limitations to Keep in Mind |
|---|
|
| Forensic Utility |
|---|
|
| Learn More about AmCache |
|---|
|
NOTE
*Old AmCache version is generally available on old systems not updated like <= Win7. The main factor isn’t the OS version but the Windows libraries on the system. If the AmCache libraries are version 6.1.x, then RecentFileCache.bcf will be present. The newer versions will use the Amcache.hve location.
** True of AmCache.hve programs and those in the older location.
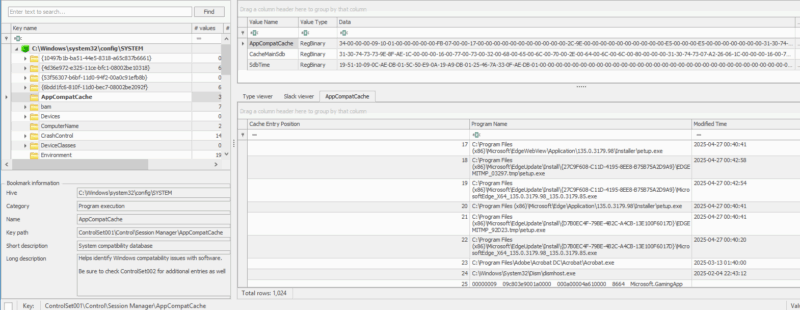
Understanding ShimCache
ShimCache (Application Compatibility Cache) is a Windows feature designed to provide backward compatibility for older applications running on newer systems. The caching information is stored in memory and written to the registry upon system shutdown. Entries are generally added to the cache if the file was executed or visible in the Windows File Explorer.
| Location | |
|---|---|
| XP | SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\AppCompatCache\AppCompatCache |
| Vista+: | SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\AppCompatCache |
| Limitations to Keep in Mind |
|---|
|
| Forensic Utility |
|---|
|
| Learn More about ShimCache |
|---|
|
NOTE
* Windows XP records 96 and Windows 2003 records 512.
** Eric Zimmerman updated AppcompatCacheParser to determine if an entry was executed based on the last 4 bytes of an entry for Windows 10+.
*** You can use volatility3 to parse ShimCache from memory.
**** This is only possible on systems before Windows 10. Starting with Windows 10, if the last 4 bytes of an entry = 1, there is a high likelihood the entry was executed, but shouldn’t be used to prove execution on its own. You can read more about this approach here.
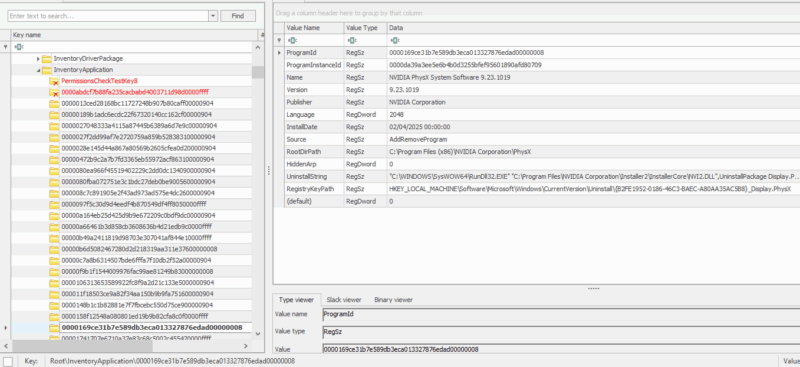
Data Captured by AmCache
NOTE
We focus on the latest version of AmCache.hve. For a detailed analysis of AmCache including all of the various versions and artifacts check out Blanche’s paper.
| InventoryApplicationFile |
|---|
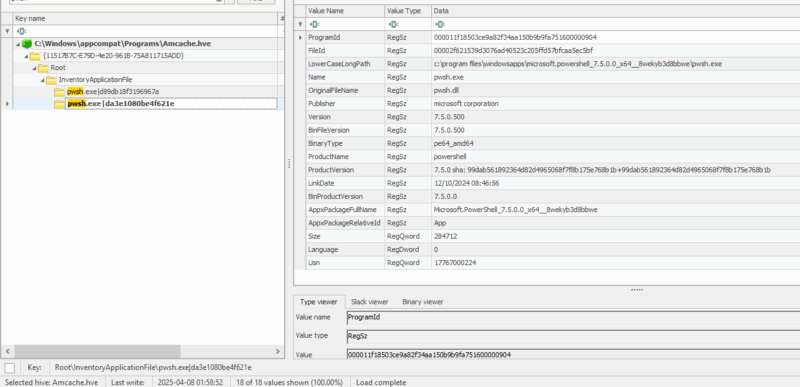 Generally contains information about files that have been executed and needed to be shimmed, exes that exist in specific folders (scanned from scheduled task), or were put on the system from an application install.
|
NOTE
* Not all entries will map to an application.
Data Captured by ShimCache
AmCache vs. ShimCache
| Feature | AmCache | ShimCache |
|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | Tracks certain PE files and installed apps (and other data). | Tracks PE files run or viewed in File Explorer. |
| When is data available | Immediately. Some data will be in transaction logs. | Updated at shutdown/reboot. |
| Key data | Rich metadata: SHA1 hashes, paths, select PE header info, install dates, etc. | Basic metadata: path, modified time, file size. |
| Location | Amcache.hve registry hive. | AppCompatCache registry entry. |
| Use cases | Prove file existence, application installation, and driver install. | Prove file existence and in certain situations execution. |
| Limitations |
|
|
Tools for Analysis
| AmCache Analysis Tools | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tool | Creator | Notes |
| AmcacheParser | Eric Zimmerman | Only exports a targeted subset of data. |
| RegRipper4 | Harlan Carvey | Regripper plugin to parse PE files and installed apps. |
| Registry Explorer | Eric Zimmerman | Plugin modules parses most interesting Amcache keys. |
| ShimCache Analysis Tools | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tool | Creator | Notes |
| AppCompatCacheParser | Eric Zimmerman | Only exports a targeted subset of data. |
| Volatility3 | Aaron Walters | Plugin to parse Shim cache entries from memory. |
| Cyber Triage | Brian Carrier | Parses shimcache entries that indicate execution and creates processes. Automatically timelined with other processes to get more context to verify actual execution. |
Other Application Compatibility Artifacts
Other artifacts related to the Windows Application Compatibility infrastructure are:
| Application Experience Event Logs | PCA (Program Compatibility Assistance) |
|---|---|
|
|